Motion sensor headlamps offer unparalleled convenience through hands-free operation. They simplify tasks in the dark by automatically turning on or off with a simple wave. This technology represents a significant upgrade from traditional headlamps, which often presented users with intricate mechanisms and required constant manual adjustments. The ease of a Motion Sensor headlamp enhances efficiency and safety, providing immediate illumination without the fumbling associated with older lighting solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Motion sensor headlamps turn on and off with a simple hand wave. This means you do not need to use your hands to press buttons.
- These headlamps make tasks easier and safer. You can keep both hands free for work or activities.
- Motion sensor headlamps are good for many uses. They help with outdoor fun, work, home projects, and emergencies.
- When you pick a headlamp, look for good battery life and brightness. Also, check if it can handle water and fits well.
- Take care of your headlamp by cleaning it. This helps it work well for a long time.
What is a Motion Sensor Headlamp?

Defining Motion Sensor Technology
A motion sensor headlamp represents an advanced personal lighting device. It integrates sensor technology to detect movement, allowing for automatic activation or deactivation of its light source. This capability provides users with hands-free control over their illumination. A PIR motion sensor, or passive infrared motion sensor, is an electronic device that identifies motion by measuring changes in infrared light emitted by objects within its range. It works by detecting variations in infrared rays caused by the movement of an object, such as a person or animal, entering its field. When such motion occurs, the change in infrared radiation is detected, and the sensor responds by generating an electric current. This is based on the principle that all objects with a temperature above absolute zero release infrared radiation, and the sensor identifies variations in this radiation when an object enters or exits its view.
The term “passive” means the sensor doesn’t emit any energy; it simply receives infrared signals.
How Motion Sensors Detect Movement
These sensors operate on a clever principle to identify movement. The PIR sensor has two slots, each sensitive to infrared (IR) radiation.
- When idle, both slots detect the same ambient IR.
- A warm body, like a human or animal, passing by first intercepts one half of the sensor, causing a positive differential change between the two halves.
- When the warm body leaves the sensing area, the reverse happens, generating a negative differential change.
- These differential change pulses are what the sensor detects as motion. This process allows the headlamp to accurately determine when a user’s hand or another object enters its detection zone.
Key Components for Hands-Free Control
Several essential electronic components work together to enable a headlamp’s motion sensing functionality. These components ensure the device can accurately detect movement and respond by controlling the light.
- Infrared emitter module
- Infrared receiver module The infrared emitter sends out an invisible beam, while the receiver detects reflections from objects. When an object, such as a hand, breaks this beam or reflects it back, the sensor registers movement. This interaction triggers the headlamp to turn its light on or off, providing intuitive, hands-free operation.
The Unmatched Convenience of Motion Sensor Operation
Eliminating Fumbling and Manual Adjustments
Traditional headlamps often present users with significant challenges, particularly in low-light conditions. Users frequently experience frustration with manual adjustments. For instance, many headlamps lack owner-accessible left-to-right adjustment, which severely limits side visibility. This becomes a critical issue on twisty country roads where drivers need to spot deer and other animals. Even with up/down adjustments and LED upgrades, side visibility often remains poor, especially on tightly curved paths. Furthermore, headlights sometimes aim too low from the factory or after repairs, making night driving feel unsafe on low beams. High beams frequently do not provide sufficient side spill, leaving peripheral areas dark.
Motion sensor headlamps directly address these common frustrations. They eliminate the need for fumbling with small buttons or dials in the dark. Users can simply wave a hand to activate or deactivate the light. This hands-free control means individuals maintain focus on their task without interruption. It also ensures consistent illumination without the distraction of manual adjustments.
Seamless Light Transitions Between Environments
Motion sensor headlamps provide effortless light transitions as users move between different environments or shift focus during a task. This capability significantly enhances workflow and efficiency. The built-in motion sensor enables hands-free operation, automatically turning the light on and off with a simple hand wave. This feature allows users to work comfortably and efficiently with both hands free. For example, a technician can easily operate the headlamp even with greasy or gloved hands, maintaining a smooth workflow without needing to stop and clean their hands to adjust the light. This seamless control ensures continuous illumination exactly when and where it is needed, adapting instantly to changing requirements.
Enhanced Hygiene and Safety with Hands-Free Use
The hands-free operation of a Motion Sensor headlamp offers substantial benefits in terms of hygiene and safety. Not touching a headlamp during tasks significantly reduces the risk of cross-contamination. This is particularly crucial in environments where maintaining sterility is paramount, such as medical or laboratory settings. The light is not adjusted during treatment, preventing the transfer of pathogens from hands to the device. Clinicians can turn the light on and off before and after donning gloves, further minimizing contamination risks.
A significant hygiene benefit is achieved through features like wave-on/off functionality. This eliminates the need to touch the battery pack or on/off switch, providing an aseptic advantage during tasks. Beyond hygiene, hands-free control also enhances safety. Users can keep both hands free for critical tasks, reducing the chance of accidents that might occur if one hand were occupied with adjusting a light. This allows for greater stability and control, especially when working in precarious positions or handling delicate equipment.
Ideal Scenarios for Your Motion Sensor Headlamp

Motion sensor headlamps offer distinct advantages across a wide array of activities, providing intuitive lighting solutions where traditional headlamps fall short. Their hands-free operation makes them an indispensable tool for anyone requiring reliable illumination without interruption.
Outdoor Adventures and Recreation
Outdoor enthusiasts find motion sensor headlamps particularly beneficial for various activities. These devices provide versatile and reliable light sources, adapting to varying light conditions encountered during adventures.
- Hiking, Camping, and Mountaineering: These activities greatly benefit from motion sensor headlamps. Users navigate challenging terrains or set up camp in the dark, requiring consistent and adaptable lighting.
- Running and Cycling: Motion sensor headlamps enhance safety for runners and cyclists. They provide consistent illumination on trails and roads, allowing users to signal without stopping or fumbling for controls.
Hands-free operation is ideal for activities where individuals need both hands. This capability allows users to control the headlamp without physically touching it, making it highly beneficial for all outdoor pursuits. Whether adjusting gear, reading a map, or preparing food, the headlamp responds to a simple wave, keeping hands free for essential tasks.
Professional and Industrial Applications
Professionals in various industries significantly improve their efficiency and safety with motion sensor headlamps. These tools streamline workflows in demanding environments.
- A motion sensor switch allows for hands-free on/off control with a simple wave.
- This feature facilitates easy operation of the headlamp even with greasy or gloved hands, ensuring a smooth workflow.
Motion sensor headlamps enhance industrial worker efficiency by enabling hands-free operation. Workers activate or deactivate the light with a simple hand wave, eliminating the need to fumble with buttons, even when wearing gloves. This feature is particularly beneficial in situations where hands are occupied, such as carrying tools, managing materials, or working in confined spaces. Mechanics, electricians, and construction workers often operate in low-light conditions or tight spaces. The ability to control light without interrupting a task or removing gloves significantly boosts productivity and reduces potential hazards.
Home Improvement and DIY Projects
Homeowners and DIY enthusiasts also discover immense value in motion sensor headlamps. These devices simplify tasks around the house, especially in poorly lit areas.
Motion sensor headlamps offer significant advantages for mechanics, especially when working in tight or dirty environments. The hands-free operation, enabled by the motion sensor, allows mechanics to turn the light on and off with a simple wave of the hand, which is particularly useful when hands are greasy or occupied. This feature ensures continuous illumination without needing to physically touch the headlamp, maintaining hygiene and efficiency. Additionally, these headlamps often provide focused illumination and wide beam coverage, enhancing visibility in confined spaces and reducing eye strain during intricate tasks.
As a mechanic, I’m always working in tight, dark spaces. This headlamp is the perfect solution—super bright, hands-free, and I don’t have to worry about adjusting it all the time.
Whether working under a sink, in an attic, or on a car engine, these headlamps provide crucial illumination. They free up both hands for holding tools, manipulating small parts, or securing fasteners. The convenience of hands-free control prevents interruptions, making home improvement projects safer and more efficient.
Emergency Preparedness and Power Outages
Emergency preparedness plans often include reliable lighting solutions. Motion sensor headlamps are crucial for emergency kits during power outages. They offer a hands-free lighting solution. The Ready Hour Rechargeable Sensor Headlamp exemplifies this utility. It is fully rechargeable, eliminating the need for batteries. Its lightweight and compact design allows for easy storage in various locations. People can keep it in emergency bags. A key feature is its true hands-free operation. A simple hand wave activates its bright white LED light. Additionally, it includes a strobe light mode. This mode can signal for help in an emergency situation.
Users consistently praise these headlamps for emergency use. One user highly recommends the Dorcy Ultra HD 650 Lumen Rechargeable Headlamp. This user experiences frequent power outages. They praise its brightness. Another review highlights its ease of use, dependability, and good quality. This user notes its various settings are useful for emergencies. A user appreciates its USB-rechargeable nature. This eliminates the need for multiple battery types. They suggest it would be great for an emergency preparedness kit. A family of farmers, campers, and hunters considers a headlamp an essential item. They praise the hands-free sensor and rechargeable feature of this particular model. They emphasize its utility for an ‘all around outdoor family’. These testimonials underscore the practical benefits of such headlamps. They provide essential illumination and convenience when traditional power sources fail.
Choosing the Right Motion Sensor Headlamp
Selecting the appropriate headlamp requires careful consideration of several key features. These features ensure the device meets specific needs and provides optimal performance for various activities.
Sensor Sensitivity and Range Considerations
When choosing a headlamp, users should evaluate the sensor’s sensitivity and its effective range. A highly sensitive sensor detects subtle movements, which prevents accidental activation or deactivation. The range determines how far away a hand gesture can control the light. Some models allow users to adjust sensitivity, which is beneficial for different environments. For instance, a lower sensitivity setting might be preferable in a busy workspace to avoid unintended light changes. A well-calibrated Motion Sensor ensures reliable and intuitive operation.
Battery Life and Rechargeable Options
Battery life is a critical factor for any headlamp. Users need to consider how long the light will last on various settings. For example, the Near Zero Motion Sensor Headlamp offers varying run times based on brightness:
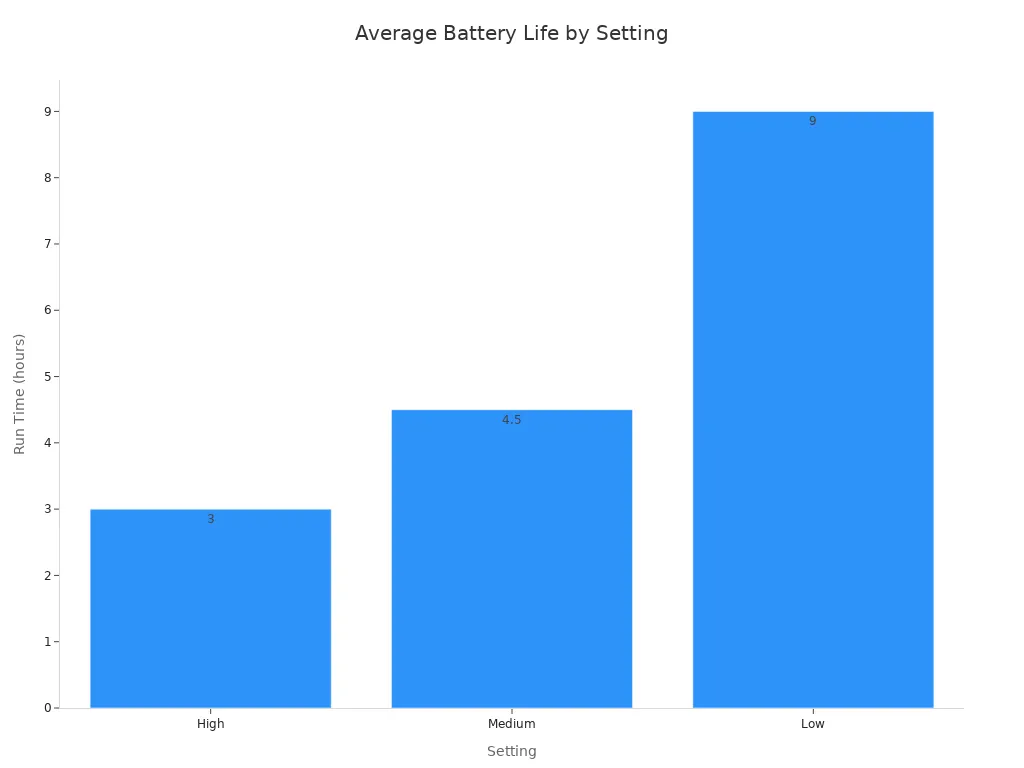
Rechargeable options offer significant advantages over disposable batteries. They reduce waste and environmental impact by eliminating the need for numerous battery purchases. Rechargeable headlamps are often lighter and more compact, requiring only a USB cable for charging instead of spare batteries. They also provide a higher, more consistent lumen output, performing better in cold conditions.
Brightness, Beam Types, and Light Modes
Brightness, measured in lumens, indicates the intensity of the light. Users should choose a lumen output suitable for their intended activities. Headlamps typically offer different beam types: flood and spot.
| Feature | Flood Beam | Spot Beam |
|---|---|---|
| Beam Angle | 45°+ (typically 90-120°) | ≤30° (typically ≤25°) |
| Coverage | Wide, diffused area; expansive | Narrow, focused circle; limited, precise |
| Light Intensity | Lower candela, spread out; high lumens | High candela, concentrated; high candela |
| Shadow Type | Soft, gradual transitions | Sharp, well-defined edges |
| Best Distance | Most effective at closer range | Effective at longer distances |
| Efficiency | High efficiency for area coverage | High efficiency for focused tasks |
| Fixture Design | Rectangular or oval housings with wider reflectors | Round heads with focused reflectors |
Flood beams illuminate a wide area, ideal for close-up tasks or general visibility. Spot beams provide a narrow, focused light for long-distance viewing. Many headlamps combine these, offering multiple light modes like high, medium, low, and strobe, to adapt to various situations.
Durability and Water Resistance (IP Ratings)
Headlamp users prioritize durability and water resistance. These features ensure reliable performance in challenging conditions. The Ingress Protection (IP) rating system indicates a device’s protection against solids and liquids. The ‘X’ in IPX signifies no testing for solid object protection. The number following ‘IPX’ specifically refers to the degree of protection against water. For headlamps, common ratings range from IPX4 to IPX8. Each rating denotes a different level of water resistance. For instance, IPX4 means the headlamp resists splashing water from all sides for five minutes. IPX5 indicates protection against low-pressure water jets. IPX6 signifies resistance to high-pressure water jets. IPX7 means the headlamp can be submerged in water up to one meter deep for 30 minutes. IPX8 denotes protection against continuous submersion at one meter or more.
| IP Rating | Water Resistance Description |
|---|---|
| IPX-0 | No water protection |
| IPX-1 | Protection against water drops like rain |
| IPX-2 | Protections against spraying water when tilted up to 15 degrees |
| IPX-3 | Protection against spraying water when tilted up to 60 degrees |
| IPX-4 | Protection against splashing water at any angle |
| IPX-5 | Protection against low-pressure spraying water at any angle |
| IPX-6 | Protection against high-pressure spraying water at any angle |
| IPX-7 | Protection against water submersion for 30 minutes at up to 1 meter depth |
| IPX-8 | Protection against continual water submersion in underwater conditions |
Comfort, Fit, and Ergonomic Design
Comfort and fit are crucial for extended headlamp use. An uncomfortable headlamp distracts users and reduces focus. Manufacturers design headlamps with adjustable straps. These straps ensure a secure fit for various head sizes and activities. Elastic straps, made from elastic materials, are common. They stretch to fit different head sizes, offering a good balance of comfort and adjustability. Some straps use nylon elastic fabric with a silicone weave. This material enhances grip and prevents slipping. Other designs feature nylon woven fabric for durability and a soft feel. An ergonomic design distributes the headlamp’s weight evenly. This minimizes pressure points and prevents fatigue. Users should look for features like padded headbands and balanced battery packs. These elements contribute to overall comfort. A well-fitting headlamp stays in place during vigorous movement. It allows users to concentrate on their tasks without constant readjustment.
Understanding and Using Your Motion Sensor Headlamp
Users can maximize the utility of their headlamps by understanding how to operate the motion sensor features. Proper activation, deactivation, and integration with other functions enhance the overall experience.
Activating and Deactivating Motion Sensor Mode
Activating the motion sensor mode on a headlamp typically involves a simple button press or a specific sequence. The SHK-1 Standard Headlamp, for instance, features a hands-free Motion Sensor mode. This allows users to activate or deactivate the light using the built-in PIR motion sensor. This eliminates the need to physically interact with the headlamp, such as removing gloves or stopping work. To deactivate motion sensor lights, users locate the ‘on time’ switch, usually under the motion sensor. They set it to any position other than the test position. Then, they flip off the main power switch connected to the light. Immediately, they flip the switch back on. This action transfers control to the main switch. To reactivate motion sensor mode, users locate the switch controlling the motion sensor light. They quickly flip it off and then on again. This rapid action restores the motion sensor function.
Preventing Accidental Activation
Accidental activation can drain batteries or cause unwanted light exposure. Manufacturers implement various mechanisms to prevent this. The Fenix HL17R headlamp features a lockout mode that prevents accidental activation, ensuring the device does not turn on unintentionally. Users can rotate the rotary switch counterclockwise to the ‘OFF’ logo to turn off the headlamp. They can also press and hold the electronic switch for 1.2 seconds to turn off the sensing function. The lamp will flash 8 times at Turbo mode, and the blue sensing function indicator light will turn off. The lamp memorizes the last selected on or off-state sensing function, so if the sensing function was off, it will remain off when turned on again.
Integrating Motion Sensing with Other Features
Modern headlamps often combine motion sensing with other advanced features. This integration creates a more versatile lighting tool. Users can typically switch between motion sensor mode and manual control, allowing flexibility for different tasks. Many headlamps also offer various brightness levels and beam types (flood or spot) that work seamlessly with the motion sensor. For example, a user might activate the motion sensor for general tasks, then manually switch to a high-lumen spot beam for detailed inspection. This combination provides optimal illumination for any situation.
Maximizing the Potential of Your Motion Sensor Headlamp
Proper Maintenance for Longevity
Proper maintenance significantly extends a motion sensor headlamp’s lifespan. Users should regularly clean the headlamp’s lens and sensor. For cleaning, gather essential tools: lint-free cleaning swabs, a specific cleaning solution, and a bulb blower. A flashlight or headlamp helps inspect the sensor for dust. To clean, find a dust-free area. Use a manual air blower to dislodge loose dust from the sensor. Avoid touching the sensor with the blower tip. For stubborn particles, use a sensor cleaning swab with one or two drops of cleaning solution. Gently move the swab across the sensor. This removes dirt without scratching.
Battery care also ensures longevity. Store batteries in a cool, dry place. This prevents corrosion and maintains effectiveness. Excessive heat accelerates chemical reactions, leading to faster depletion. Cold temperatures cause batteries to lose charge quickly. Remove rechargeable batteries for long-term storage. This prevents unintentional drainage. Store them in original packaging or a battery case to avoid short circuits.
Tips for Optimal Performance
Users can optimize headlamp performance by understanding environmental factors. Reflective surfaces, like glass or metal, can distort sensor readings. Maintain a minimum distance of 1.5 meters from such surfaces. Light reflecting at steep angles also causes unstable readings. Tilt the sensor or use baffles to block glare. Avoid installing sensors directly facing east or west.
Sudden airflow and temperature shifts, near HVAC exhausts or generators, cause false triggers. Maintain a 1-meter clearance from these sources. High temperatures and humidity accelerate sensor wear. Use IP65-rated controllers or higher. Install sensors under canopies to mitigate these issues. Dust accumulation blocks light sensors. Industrial gases damage internal components. Use IP66-rated or sealed controllers. Regular cleaning every 6-12 months helps. Ensure the sensor remains clear of obstructions like foliage or walls.
Troubleshooting Common Motion Sensor Issues
Motion sensor headlamps occasionally experience issues. If the sensor triggers unexpectedly, check for environmental factors. Sudden temperature changes or reflective surfaces often cause false activations. Clean the sensor lens if the headlamp fails to detect movement. Dust or dirt on the sensor can block its detection capabilities. Ensure the headlamp’s battery has sufficient charge. Low power can affect sensor responsiveness. If problems persist, consult the headlamp’s user manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Motion sensor headlamps redefine personal lighting. They offer unparalleled hands-free convenience. These devices provide significant advantages in efficiency, safety, and ease of use. This applies across a wide range of activities. Motion sensor headlamps are an indispensable tool. They deliver quick, intuitive light control. This makes them highly valuable in diverse environments. Users benefit from their advanced functionality.
FAQ
How long does the battery typically last on a motion sensor headlamp?
Battery life varies significantly. It depends on the brightness setting and specific model. High-lumen modes consume more power. Many rechargeable models offer several hours of use. Lower settings extend battery life considerably.
Can I use a motion sensor headlamp in wet conditions?
Yes, many motion sensor headlamps are water-resistant. Check the IP (Ingress Protection) rating. An IPX4 rating protects against splashes. Higher ratings, like IPX7 or IPX8, allow for submersion. Always verify the specific model’s rating.
How do I prevent accidental activation of the motion sensor?
Many headlamps feature a lockout mode. This prevents unintended activation. Users can also deactivate the motion sensor function. They switch to manual control when not needed. Proper storage also helps avoid accidental triggers.
What is the best way to clean the motion sensor on my headlamp?
Gently wipe the sensor lens with a soft, lint-free cloth. Use a small amount of mild cleaning solution if necessary. Avoid abrasive materials. Dust or dirt on the sensor can impair its detection capabilities. Regular cleaning ensures optimal performance.
Do motion sensor headlamps work with gloves on?
Yes, motion sensor headlamps are designed for hands-free operation. They detect movement from a hand wave. This works effectively even when wearing gloves. This feature is particularly useful in cold or dirty environments.
Post time: Jan-06-2026
 fannie@nbtorch.com
fannie@nbtorch.com +0086-0574-28909873
+0086-0574-28909873





